🎯 Semantic Entropy#
This demo illustrates a state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification (UQ) approach known as semantic entropy. The token-probability-based semantic entropy method combines elements of black-box UQ (which generates multiple responses from the same prompt) and white-box UQ (which uses token probabilities of those generated responses) to compute entropy values and associated confidence scores. The discrete semantic entropy method is similar but functions solely as a black-box UQ method, as it does not require token probabilities. Both methods were proposed by Farquhar et al. (2024) and are demonstrated in this notebook.
📊 What You’ll Do in This Demo#
1
Set up LLM and prompts.
Set up LLM instance and load example data prompts.
2
Generate LLM Responses and Confidence Scores
Generate and score LLM responses to the example questions using the SemanticEntropy() class.
3
Evaluate Hallucination Detection Performance
Visualize model accuracy at different thresholds of the semantic entropy-based confidence scores. Compute precision, recall, and F1-score of hallucination detection.
⚖️ Advantages & Limitations#
Pros
Universal Compatibility: Works with any LLM
Intuitive: Easy to understand and implement
No Internal Access Required: Doesn’t need token probabilities or model internals
Cons
Higher Cost: Requires multiple generations per prompt
Slower: Multiple generations and comparison calculations increase latency
[1]:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score, f1_score
from uqlm.utils import load_example_dataset, plot_model_accuracies, Tuner
from uqlm import SemanticEntropy
## 1. Set up LLM and Prompts
In this demo, we will illustrate this approach using a set of multiple choice questions from the CommonSense QA benchmark. To implement with your use case, simply replace the example prompts with your data.
[ ]:
# Load example dataset (csqa)
csqa = load_example_dataset("csqa", n=200)
csqa.head()
Loading dataset - csqa...
Processing dataset...
Dataset ready!
| question | answer | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Q: The sanctions against the school were a pun... | A |
| 1 | Q: Sammy wanted to go to where the people were... | B |
| 2 | Q: To locate a choker not located in a jewelry... | A |
| 3 | Q: Google Maps and other highway and street GP... | D |
| 4 | Q: The fox walked from the city into the fores... | C |
[4]:
# Define prompts
MCQ_INSTRUCTION = "You will be given a multiple choice question. Return only the letter of the response with no additional text or explanation.\n"
prompts = [MCQ_INSTRUCTION + prompt for prompt in csqa.question]
In this example, we use AzureChatOpenAI to instantiate our LLM, but any LangChain Chat Model may be used. Be sure to replace with your LLM of choice.
[5]:
## AzureChatOpenAI example
# import sys
# !{sys.executable} -m pip install langchain-openai
# # User to populate .env file with API credentials
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(
deployment_name="gpt-4.1-mini",
openai_api_type="azure",
openai_api_version="2024-02-15-preview",
temperature=1, # User to set temperature
)
## 2. Generate responses and confidence scores
SemanticEntropy() - Generate LLM responses and compute consistency-based confidence scores for each response.#
📋 Class Attributes#
Parameter | Type & Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
llm | BaseChatModeldefault=None | A langchain llm |
device | str or torch.devicedefault=”cpu” | Specifies the device that NLI model use for prediction. Only applies to ‘semantic_negentropy’, ‘noncontradiction’ scorers. Pass a torch.device to leverage GPU. |
use_best | booldefault=True | Specifies whether to swap the original response for the uncertainty-minimized response among all sampled responses based on semantic entropy clusters. Only used if |
system_prompt | str or Nonedefault=”You are a helpful assistant.” | Optional argument for user to provide custom system prompt for the LLM. |
max_calls_per_min | intdefault=None | Specifies how many API calls to make per minute to avoid rate limit errors. By default, no limit is specified. |
length_normalize | boolbool, default=True | Determines whether response probabilities are length-normalized. Recommended to set as True when longer responses are expected. |
use_n_param | booldefault=False | Specifies whether to use n parameter for BaseChatModel. Not compatible with all BaseChatModel classes. If used, it speeds up the generation process substantially when num_responses is large. |
postprocessor | callabledefault=None | A user-defined function that takes a string input and returns a string. Used for postprocessing outputs. |
sampling_temperature | floatdefault=1 | The ‘temperature’ parameter for LLM model to generate sampled LLM responses. Must be greater than 0. |
nli_model_name | strdefault=”microsoft/deberta-large-mnli” | Specifies which NLI model to use. Must be acceptable input to AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained() and AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(). |
max_length | intdefault=2000 | Specifies the maximum allowed string length for LLM responses for NLI computation. Responses longer than this value will be truncated in NLI computations to avoid OutOfMemoryError. |
return_responses | strdefault=”all” | If a postprocessor is used, specifies whether to return only postprocessed responses, only raw responses, or both. Specified with ‘postprocessed’, ‘raw’, or ‘all’, respectively. |
🔍 Parameter Groups#
🧠 LLM-Specific
llm
system_prompt
sampling_temperature
📊 Confidence Scores
length_normalize
nli_model_name
use_best
postprocessor
🖥️ Hardware
device
⚡ Performance
max_calls_per_min
use_n_param
💻 Usage Examples#
# Basic usage with default parameters
se = SemanticEntropy(llm=llm)
# Using GPU acceleration, default scorers
se = SemanticEntropy(llm=llm, device=torch.device("cuda"))
# High-throughput configuration with rate limiting
se = SemanticEntropy(llm=llm, max_calls_per_min=200, use_n_param=True)
[6]:
import torch
# Set the torch device
if torch.cuda.is_available(): # NVIDIA GPU
device = torch.device("cuda")
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available(): # macOS
device = torch.device("mps")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu") # CPU
print(f"Using {device.type} device")
Using mps device
[7]:
se = SemanticEntropy(
llm=llm,
max_calls_per_min=100, # set value to avoid rate limit error
device=device, # use if GPU available
length_normalize=True,
)
🔄 Class Methods#
Method | Description & Parameters |
|---|---|
SemanticEntropy.generate_and_score | Generate LLM responses, sampled LLM (candidate) responses, and compute confidence scores for the provided prompts. Parameters:
Returns: UQResult containing data (prompts, responses, sampled responses, and confidence scores) and metadata 💡 Best For: Complete end-to-end uncertainty quantification when starting with prompts. |
SemanticEntropy.score | Compute confidence scores on provided LLM responses. Should only be used if responses and sampled responses are already generated. Parameters:
Returns: UQResult containing data (responses, sampled responses, and confidence scores) and metadata 💡 Best For: Computing uncertainty scores when responses, sampled responses, and logprobs are already generated elsewhere. |
[8]:
results = await se.generate_and_score(prompts=prompts, num_responses=10)
# # alternative approach: directly score if responses already generated
# results = se.score(responses=responses, sampled_responses=sampled_responses)
The LLM instance used here returns token probabilities during the response generation. In such scenario, SemanticEntropy class computes response probabilty in two ways: 1) Discrete semantic entropy: Equal probability to each response cluster and 2) Token-probability-based semantic entropy: Uses token probability to compute probability of each response cluster.
[9]:
result_df = results.to_df()
result_df.head(5)
[9]:
| response | sampled_responses | prompt | discrete_entropy_value | discrete_confidence_score | tokenprob_entropy_value | tokenprob_confidence_score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | E | [E, A, E, E, A, E, A, E, E, A] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.655482 | 0.726643 | 0.668995 | 0.721007 |
| 1 | B | [B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 2 | B | [B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 3 | D | [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 4 | C | [C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 |
## 3. Evaluate Hallucination Detection Performance
To evaluate hallucination detection performance, we ‘grade’ the responses against an answer key. Note the check_letter_match function is specific to our task (multiple choice). If you are using your own prompts/questions, update the grading method accordingly.
[10]:
# Populate correct answers and grade responses
result_df["answer"] = csqa.answer
def check_letter_match(response: str, answer: str):
return response.strip().lower()[0] == answer[0].lower()
result_df["response_correct"] = [check_letter_match(r, a) for r, a in zip(result_df["response"], csqa["answer"])]
result_df.head()
[10]:
| response | sampled_responses | prompt | discrete_entropy_value | discrete_confidence_score | tokenprob_entropy_value | tokenprob_confidence_score | answer | response_correct | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | E | [E, A, E, E, A, E, A, E, E, A] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.655482 | 0.726643 | 0.668995 | 0.721007 | A | False |
| 1 | B | [B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | B | True |
| 2 | B | [B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | A | False |
| 3 | D | [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | D | True |
| 4 | C | [C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C, C] | You will be given a multiple choice question. ... | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | C | True |
[15]:
print(f"""Baseline LLM accuracy: {np.mean(result_df["response_correct"])}""")
Baseline LLM accuracy: 0.775
3.1 Filtered LLM Accuracy Evaluation#
Here, we explore ‘filtered accuracy’ as a metric for evaluating the performance of our confidence scores. Filtered accuracy measures the change in LLM performance when responses with confidence scores below a specified threshold are excluded. By adjusting the confidence score threshold, we can observe how the accuracy of the LLM improves as less certain responses are filtered out.
We will plot the filtered accuracy across various confidence score thresholds to visualize the relationship between confidence and LLM accuracy. This analysis helps in understanding the trade-off between response coverage (measured by sample size below) and LLM accuracy, providing insights into the reliability of the LLM’s outputs.
Discrete Semantic Entropy#
[16]:
# Discrete Semantic Entropy
plot_model_accuracies(scores=result_df.discrete_confidence_score, correct_indicators=result_df.response_correct, display_percentage=True)
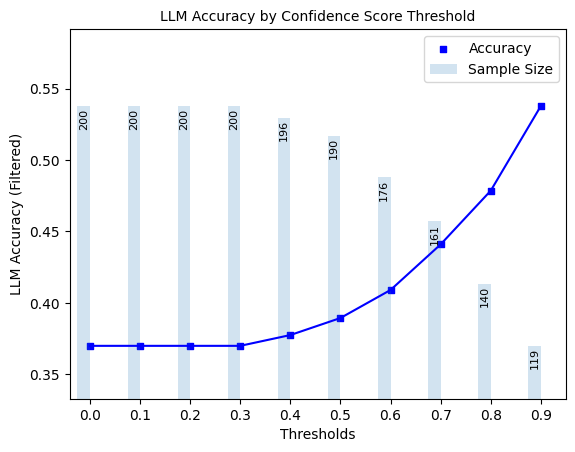
Discrete Semantic Entropy#
[13]:
plot_model_accuracies(scores=result_df.tokenprob_confidence_score, correct_indicators=result_df.response_correct, display_percentage=True)
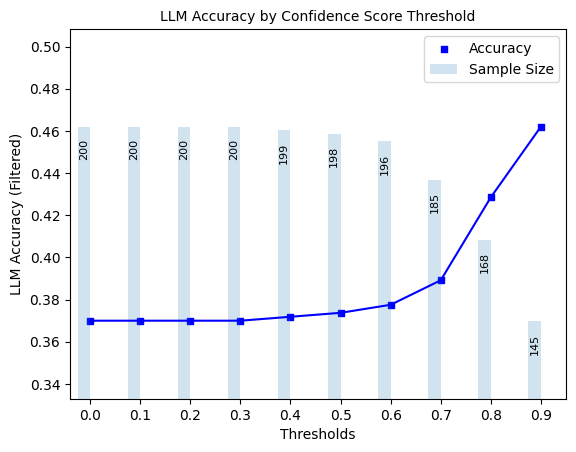
3.2 Precision, Recall, F1-Score of Hallucination Detection#
Lastly, we compute the optimal threshold for binarizing confidence scores, using F1-score as the objective. Using these thresholds, we compute precision, recall, and F1-score for our two semantic entropy-based scorer predictions of whether responses are correct.
[ ]:
# instantiate UQLM tuner object for threshold selection
split = len(result_df) // 2
t = Tuner()
correct_indicators = (result_df.response_correct) * 1 # Whether responses is actually correct
metric_values = {"Precision": [], "Recall": [], "F1-score": []}
optimal_thresholds = []
for confidence_score in ["discrete_confidence_score", "tokenprob_confidence_score"]:
# tune threshold on first half
y_scores = result_df[confidence_score]
y_scores_tune = y_scores[0:split]
y_true_tune = correct_indicators[0:split]
best_threshold = t.tune_threshold(y_scores=y_scores_tune, correct_indicators=y_true_tune, thresh_objective="fbeta_score")
y_pred = [(s > best_threshold) * 1 for s in y_scores] # predicts whether response is correct based on confidence score
optimal_thresholds.append(best_threshold)
# evaluate on last half
y_true_eval = correct_indicators[split:]
y_pred_eval = y_pred[split:]
metric_values["Precision"].append(precision_score(y_true=y_true_eval, y_pred=y_pred_eval))
metric_values["Recall"].append(recall_score(y_true=y_true_eval, y_pred=y_pred_eval))
metric_values["F1-score"].append(f1_score(y_true=y_true_eval, y_pred=y_pred_eval))
# print results
header = f"{'Metrics':<25}" + "".join([f"{scorer_name:<35}" for scorer_name in ["discrete_confidence_score", "tokenprob_confidence_score"]])
print("=" * len(header) + "\n" + header + "\n" + "-" * len(header))
for metric in metric_values.keys():
print(f"{metric:<25}" + "".join([f"{round(x_, 3):<35}" for x_ in metric_values[metric]]))
print("-" * len(header))
print(f"{'F-1 optimal threshold':<25}" + "".join([f"{round(x_, 3):<35}" for x_ in optimal_thresholds]))
print("=" * len(header))
===============================================================================================
Metrics discrete_confidence_score tokenprob_confidence_score
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Precision 0.779 0.773
Recall 0.984 0.977
F1-score 0.87 0.863
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
F-1 optimal threshold 0.72 0.73
===============================================================================================
4. Scorer Definitions#
Below are the definitions of the two confidence scores used in this demo.
Normalized Semantic Negentropy (Discrete)#
Normalized Semantic Negentropy (NSN) normalizes the standard computation of discrete semantic entropy to be increasing with higher confidence and have [0,1] support. Under this approach, responses are clustered using an NLI model based on mutual entailment. After obtaining the set of clusters \(\mathcal{C}\), semantic entropy is computed as:
where \(P(C|y_i, \tilde{\mathbf{y}}_i)\) is calculated as the probability a randomly selected response $y \in `{y_i} :nbsphinx-math:cup :nbsphinx-math:tilde{mathbf{y}}`_i $ belongs to cluster \(C\), and \(\mathcal{C}\) denotes the full set of clusters of \(\{y_i\} \cup \tilde{\mathbf{y}}_i\).
To ensure that we have a normalized confidence score with \([0,1]\) support and with higher values corresponding to higher confidence, we implement the following normalization to arrive at Normalized Semantic Negentropy (NSN):
where \(\log m\) is included to normalize the support.
Normalized Semantic Negentropy (Token-Probability-Based)#
For this version, the formula is the same as above except \(P(C|y_i, \tilde{\mathbf{y}}_i)\) is calculated as the average across response-level sequence probabilities (normalized or otherwise). For more on semantic entropy, refer to Farquhar et al., 2024; Kuhn et al., 2023, and for more on our normalized version, refer to Bouchard & Chauhan, 2025.
© 2025 CVS Health and/or one of its affiliates. All rights reserved.