🎯 Graph-Based Uncertainty Quantification (Long-Text)#
Graph-based scorers decompose original and sampled responses into claims, obtain the union of unique claims across all responses, and compute graph centrality metrics on the bipartite graph of claim-response entailment to measure uncertainty. This demo provides an illustration of how to use these methods with uqlm. The available scorers and papers from which they are adapted are below:
Closeness Centrality (Jiang et al., 2024)
Betweenness Centrality (Jiang et al., 2024)
PageRank (Jiang et al., 2024)
Degree Centrality (Zhang et al., 2024)
Harmonic Centrality
Laplacian Centrality
📊 What You’ll Do in This Demo#
1
Set up LLM and prompts.
Set up LLM instance and load example data prompts.
2
Generate LLM Responses and Confidence Scores
Generate responses and compute claim-level confidence scores using the LongTextGraph() class.
3
Evaluate Hallucination Detection Performance
Grade claims with FactScoreGrader class and evaluate claim-level hallucination detection.
⚖️ Advantages & Limitations#
Pros
Universal Compatibility: Works with any LLM without requiring token probability access
Fine-Grained Scoring: Score at sentence or claim-level to localize likely hallucinations
Uncertainty-aware decoding: Improve factual precision by dropping high-uncertainty claims
Cons
Higher Cost: Requires multiple generations per prompt
Slower: Multiple generations and comparison calculations increase latency
Important note: Graph-based scoring requires networkx package. Please ensure networkx is installed before running this notebook.
[1]:
# import sys
# !{sys.executable} -m pip install networkx
import numpy as np
from uqlm import LongTextGraph
from uqlm.utils import load_example_dataset, display_response_refinement, claims_dicts_to_lists, plot_model_accuracies
from uqlm.longform import FactScoreGrader
1. Set up LLM and Prompts#
In this demo, we will illustrate this approach using the FactScore longform QA dataset. To implement with your use case, simply replace the example prompts with your data.
[2]:
# Load example dataset (FactScore)
factscore = load_example_dataset("factscore", n=1)[["hundredw_prompt", "wikipedia_text"]].rename(columns={"hundredw_prompt": "prompt"})
factscore.head()
Loading dataset - factscore...
Processing dataset...
Dataset ready!
[2]:
| prompt | wikipedia_text | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tell me a bio of Suthida within 100 words.\n | Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana (Thai: สมเด็จ... |
In this example, we use AzureChatOpenAI to instantiate our LLM, but any LangChain Chat Model may be used. Be sure to replace with your LLM of choice.
[3]:
from langchain_google_vertexai import ChatVertexAI
gemini_flash = ChatVertexAI(model="gemini-2.5-flash")
2. Generate LLM Responses and Claim/Sentence-Level Confidence Scores#
LongTextGraph() - Generate long-text LLM responses, decompose into claims or sentences, and measure entailment among sampled responses.#
📋 Class Attributes#
Parameter | Type & Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
llm | BaseChatModeldefault=None | A langchain llm |
scorers | List[str]default=None | Specifies which graph-based scorers to include. Must be subset of [“degree_centrality”, “betweenness_centrality”, “closeness_centrality”, “page_rank”, “laplacian_centrality”, “harmonic_centrality”]. If None, defaults to [“closeness_centrality”]. |
aggregation | strdefault=”mean” | Specifies how to aggregate claim/sentence-level scores to response-level scores. Must be one of ‘min’ or ‘mean’. |
response_refinement | booldefault=False | Specifies whether to refine responses with uncertainty-aware decoding. This approach removes claims with confidence scores below the response_refinement_threshold and uses the claim_decomposition_llm to reconstruct the response from the retained claims. For more details, refer to Jiang et al., 2024: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.20783 |
claim_filtering_scorer | Optional[str]default=None | Specifies which scorer to use to filter claims if response_refinement is True. If not provided, defaults to the first element of self.scorers. |
claim_decomposition_llm | BaseChatModeldefault=None | A langchain llm |
nli_llm | BaseChatModeldefault=None | A LangChain chat model for LLM-based NLI inference. If provided, takes precedence over nli_model_name. Only used for mode=”unit_response” |
device | str or torch.devicedefault=None | Specifies the device that NLI model use for prediction. If None, detects and returns the best available PyTorch device. Prioritizes CUDA (NVIDIA GPU), then MPS (macOS), then CPU. |
system_prompt | str or Nonedefault=”You are a helpful assistant.” | Optional argument for user to provide custom system prompt for the LLM. |
max_calls_per_min | intdefault=None | Specifies how many API calls to make per minute to avoid rate limit errors. By default, no limit is specified. |
use_n_param | booldefault=False | Specifies whether to use n parameter for BaseChatModel. Not compatible with all BaseChatModel classes. If used, it speeds up the generation process substantially when num_responses is large. |
sampling_temperature | floatdefault=1 | The ‘temperature’ parameter for LLM to use when generating sampled LLM responses. Must be greater than 0. |
nli_model_name | strdefault=”microsoft/deberta-large-mnli” | Specifies which NLI model to use. Must be acceptable input to AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained() and AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(). |
max_length | intdefault=2000 | Specifies the maximum allowed string length for LLM responses for NLI computation. Responses longer than this value will be truncated in NLI computations to avoid OutOfMemoryError. |
🔍 Parameter Groups#
🧠 LLM-Specific
llm
system_prompt
sampling_temperature
claim_decomposition_llm
nli_llm
📊 Confidence Scores
granularity
scorers
mode
aggregation
response_refinement
response_refinement_threshold
🖥️ Hardware
device
⚡ Performance
max_calls_per_min
use_n_param
```
[4]:
ltg = LongTextGraph(
llm=gemini_flash,
aggregation="mean", # switch to 'min' for more conservative scoring
response_refinement=True, # whether to filter out low-confidence claims
scorers=["degree_centrality"],
# response_refinement_threshold=1 / 3, # adjust claim filtering threshold based on risk preferences
# max_calls_per_min=80,
)
🔄 Class Methods#
Method | Description & Parameters |
|---|---|
BlackBoxUQ.generate_and_score | Generate LLM responses, sampled LLM (candidate) responses, and compute confidence scores for the provided prompts. Parameters:
Returns: UQResult containing data (prompts, responses, sampled responses, and confidence scores) and metadata 💡 Best For: Complete end-to-end uncertainty quantification when starting with prompts. |
BlackBoxUQ.score | Compute confidence scores on provided LLM responses. Should only be used if responses and sampled responses are already generated. Parameters:
Returns: UQResult containing data (responses, sampled responses, and confidence scores) and metadata 💡 Best For: Computing uncertainty scores when responses are already generated elsewhere. |
[5]:
results = await ltg.generate_and_score(
prompts=factscore.prompt.to_list(),
num_responses=5, # choose num_responses based on cost and latency requirements (higher means better hallucination detection but more cost and latency)
)
[7]:
result_df = results.to_df()
result_df.head(5)
[7]:
| prompt | response | sampled_responses | degree_centrality | claims_data | refined_response | refined_degree_centrality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tell me a bio of Suthida within 100 words.\n | Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is the ... | [Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is the... | 0.7389 | [{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalaks... | Born Suthida Tidjai, Queen Suthida Bajrasudhab... | 0.76798 |
Response refinement#
Response refinement works by dropping claims with confidence scores (specified with claim_filtering_scorer) below a specified threshold (specified with response_refinement_threshold) and reconstructing the response from the retained claims.

To illustrate how the response refinement operates, let’s view an example. We first view the fine-grained claim-level data, including the claims in the original response, the claim-level confidence scores, and whether each claim was removed during the response refinement process.
[8]:
result_df.claims_data[0]
[8]:
[{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is the current Queen Consort of Thailand.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.75818,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is married to King Maha Vajiralongkorn.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.92884,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was born Suthida Tidjai.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.82817,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai initially worked as a flight attendant.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.9895,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai worked for Thai Airways.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.98485,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai later joined the Royal Thai Army.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.98098,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai rapidly ascended through the ranks.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.97471,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai became a general.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.98176,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "Suthida Tidjai's marriage occurred in 2019.",
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.97804,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "Suthida Tidjai served as the deputy commander of the King's Royal Guard.",
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.4668,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "Suthida Tidjai served as the deputy commander of the King's Royal Guard prior to her marriage.",
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.44859,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai demonstrated a distinguished career in aviation.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.79436,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai demonstrated a distinguished career in military service.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.94568,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai became Queen.',
'original_response': True,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.91839,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana married King Vajiralongkorn on May 1, 2019.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.33107,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana plays a supportive role alongside the monarch.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.164,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'King Vajiralongkorn had a coronation.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.77994,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Maha Vajiralongkorn was then-Crown Prince.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16263,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana plays a supportive role in ceremonies.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16398,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana joined the Royal Thai Army in 2010.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.33148,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana served as a bodyguard to then-Crown Prince Maha Vajiralongkorn.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16499,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana plays a supportive role in royal duties.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16397,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was officially named Queen Consort of Thailand.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.70987,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "The marriage occurred just days before King Vajiralongkorn's coronation.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.81827,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'King Maha Vajiralongkorn is Rama X.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.36703,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was formally crowned as Queen.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.2776,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'The marriage was announced in May 2019.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.59038,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was crowned during King Vajiralongkorn's official coronation.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.29731,
'removed': True},
{'claim': "The marriage was announced days before King Vajiralongkorn's official coronation.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.49288,
'removed': False},
{'claim': 'The marriage of Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana and King Maha Vajiralongkorn was announced.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.49703,
'removed': False},
{'claim': "Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana became deputy commander of the King's Royal Security Command.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.31186,
'removed': True},
{'claim': "Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana became commander of the King's security unit.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.15637,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'The marriage was announced on May 1, 2019.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16573,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai secretly married King Vajiralongkorn.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16514,
'removed': True},
{'claim': "Suthida Tidjai's path is remarkable.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.14438,
'removed': True},
{'claim': 'Suthida Tidjai was born in 1978.',
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.16578,
'removed': True},
{'claim': "Suthida Tidjai's path is a prominent feature of her life.",
'original_response': False,
'scorer_type': 'graphuq',
'degree_centrality': 0.15942,
'removed': True}]
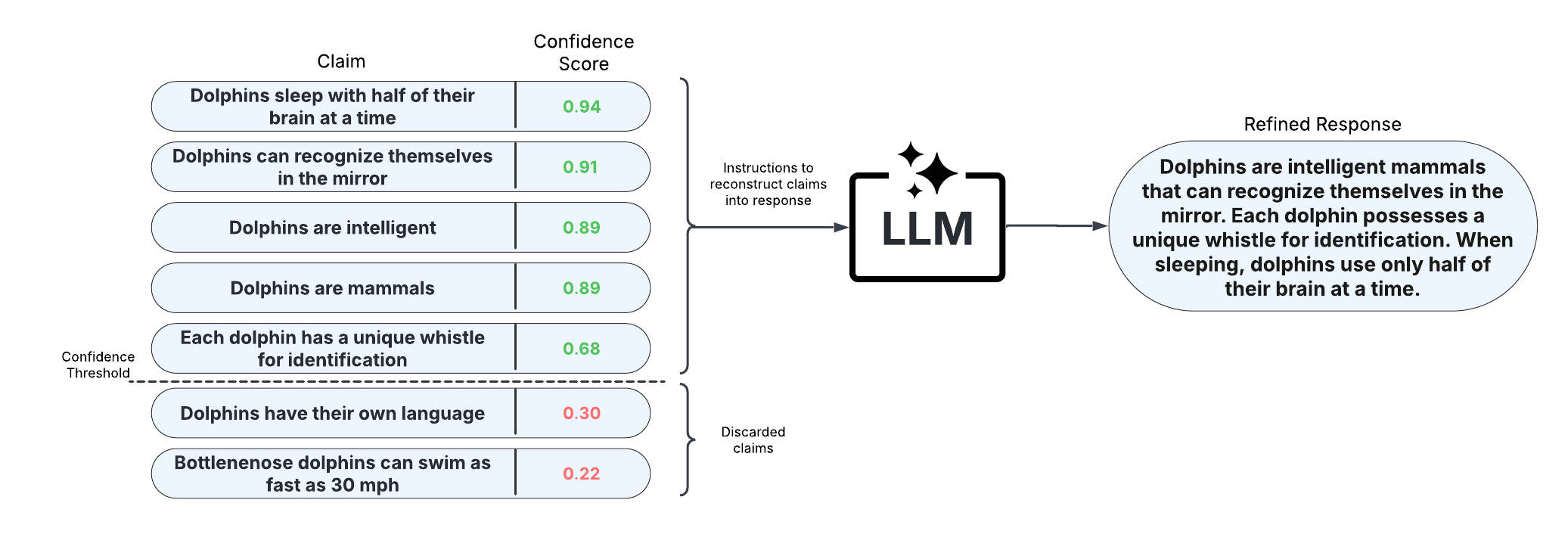
We can then visualize the response refinement process for this response using the display_response_refinement. This shows the original response vs. the refined response and identifies which claims were removed due to low confidence.
[8]:
display_response_refinement(original_text=result_df.response[0], claims_data=result_df.claims_data[0], refined_text=result_df.refined_response[0])
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Response Refinement Example
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
╭─────────────────────────────────────────────── Original Response ───────────────────────────────────────────────╮ │ Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana, born on June 3, 1978, is the Queen of Thailand. She became queen following │ │ her marriage to King Maha Vajiralongkorn (Rama X) on May 1, 2019. │ │ │ │ Before becoming queen, Suthida was known for her service in the Thai military and royal security. She joined │ │ the Thai military, where she eventually rose to the rank of General. Her notable role was as the Deputy │ │ Commander of the King’s Own Bodyguard Battalion. Suthida was also appointed as the Commander of the Special │ │ Operations Unit of the King’s Guard in 2013, and later, she was made the Commander of the Royal Thai │ │ Aide-de-Camp Department. │ │ │ │ Her service to the royal family and her close association with King Vajiralongkorn began during his time as │ │ Crown Prince. Suthida was appointed as a General in the Royal Thai Army in December 2016, shortly after │ │ Vajiralongkorn ascended to the throne. │ │ │ │ Queen Suthida's royal name, bestowed upon her after marriage, is Her Majesty Queen Suthida │ │ Bajrasudhabimalalakshana. The marriage and her subsequent coronation as queen were part of the elaborate royal │ │ ceremonies that solidified her position as the consort of the reigning monarch. │ │ │ │ Queen Suthida is known for her dignity and dedication to her roles both in royal duties and her previous │ │ military service. Her work and public engagements often highlight charitable activities and support for various │ │ social causes within Thailand. │ ╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭────────────────────────────────────── Low-Confidence Claims to be Removed ──────────────────────────────────────╮ │ • Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana's notable role was as the Deputy Commander of the King’s Own Bodyguard │ │ Battalion. │ │ • Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was appointed as the Commander of the Special Operations Unit of the King’s │ │ Guard in 2013. │ │ • Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was made the Commander of the Royal Thai Aide-de-Camp Department. │ │ • Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana's service to the royal family began during Vajiralongkorn's time as Crown │ │ Prince. │ │ • Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana was appointed as a General in the Royal Thai Army in December 2016. │ │ • Vajiralongkorn ascended to the throne shortly before December 2016. │ │ • The marriage and Queen Suthida's subsequent coronation were part of the elaborate royal ceremonies. │ │ • The elaborate royal ceremonies solidified Queen Suthida's position as the consort of the reigning monarch. │ │ • Queen Suthida is known for her dignity. │ │ • Queen Suthida is known for her dedication to her roles in royal duties. │ │ • Queen Suthida is known for her dedication to her previous military service. │ │ • Queen Suthida's work and public engagements often highlight charitable activities in Thailand. │ │ • Queen Suthida's work and public engagements often support various social causes within Thailand. │ ╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─────────────────────────────────────────────── Refined Response ────────────────────────────────────────────────╮ │ Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana, born on June 3, 1978, is the Queen of Thailand. She became queen following │ │ her marriage to King Maha Vajiralongkorn on May 1, 2019, and upon marriage, she was bestowed with the royal │ │ name Her Majesty Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana. Before her ascension to the throne, Queen Suthida was │ │ recognized for her dedicated service in the Thai military, where she rose to the rank of General, and in royal │ │ security. Her military career and commitment to royal security played a significant role in her rise to │ │ prominence, ultimately leading to her role as queen. │ ╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
3. Evaluate Hallucination Detection Performance#
To evaluate hallucination detection performance, we ‘grade’ the atomic claims in the responses against an answer key. Here, we use UQLM’s out-of-the-box FactScoreGrader, which can be used with LangChain Chat Model. If you are using your own prompts/questions, be sure to update the grading method accordingly.
[10]:
# set up the LLM grader
from langchain_google_vertexai import ChatVertexAI
gemini_flash = ChatVertexAI(model="gemini-2.5-flash")
grader = FactScoreGrader(llm=gemini_flash)
Before grading, we need to have claims formatted in list of lists where each interior list corresponds to a generated response.
[11]:
# Convert claims to list of lists
claims_data_lists = claims_dicts_to_lists(result_df.claims_data.tolist())
[12]:
# grade original responses against the answer key using the grader
result_df["claim_grades"] = await grader.grade_claims(claim_sets=claims_data_lists["claim"], answers=factscore["wikipedia_text"].to_list())
result_df["answer"] = factscore["wikipedia_text"]
result_df.head(5)
[12]:
| prompt | response | sampled_responses | degree_centrality | claims_data | refined_response | refined_degree_centrality | claim_grades | answer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tell me a bio of Suthida within 100 words.\n | Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is the ... | [Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana, born ... | 0.855632 | [{'claim': 'Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalaks... | Queen Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana is the ... | 0.773060 | [True, True, True, True, True, False, True, Tr... | Suthida Bajrasudhabimalalakshana (Thai: สมเด็จ... |
| 1 | Tell me a bio of Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo w... | Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo, known as "El Padr... | [Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo, known as "El Pad... | 0.569820 | [{'claim': 'Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo was kn... | Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo, a Mexican drug lo... | 0.731845 | [True, True, True, True, True, True, False, Fa... | Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo (born January 8, 1... |
| 2 | Tell me a bio of Iggy Azalea within 100 words.\n | Amethyst Amelia Kelly, known as Iggy Azalea, i... | [Amethyst Amelia Kelly, known professionally a... | 0.753417 | [{'claim': 'Amethyst Amelia Kelly is an Austra... | Amethyst Amelia Kelly, widely recognized as Ig... | 0.720593 | [True, True, True, True, True, True, True, Tru... | Amethyst Amelia Kelly (born 7 June 1990), know... |
| 3 | Tell me a bio of Fernando da Costa Novaes with... | Fernando da Costa Novaes is a distinguished Br... | [Fernando da Costa Novaes (born 1941) is a dis... | 0.648004 | [{'claim': 'Fernando da Costa Novaes is a hist... | Fernando da Costa Novaes is a distinguished Br... | 0.836937 | [False, True, True, False, True, True, False, ... | Fernando da Costa Novaes (April 6, 1927 – Marc... |
| 4 | Tell me a bio of Jan Zamoyski within 100 words.\n | Jan Zamoyski (1542–1605) was a preeminent Poli... | [Jan Zamoyski (1542–1605) was a paramount figu... | 0.706531 | [{'claim': 'Jan Zamoyski was born in 1542.', '... | Jan Zamoyski, born in 1542 and passing away in... | 0.757186 | [True, True, True, True, True, True, True, Tru... | Jan Sariusz Zamoyski (Latin: Ioannes Zamoyski ... |
[14]:
all_claim_scores, all_claim_grades = [], []
for i in range(len(result_df)):
all_claim_scores.extend(claims_data_lists["degree_centrality"][i])
all_claim_grades.extend(result_df["claim_grades"][i])
print(f"""Baseline LLM accuracy: {np.mean(all_claim_grades)}""")
Baseline LLM accuracy: 0.6257668711656442
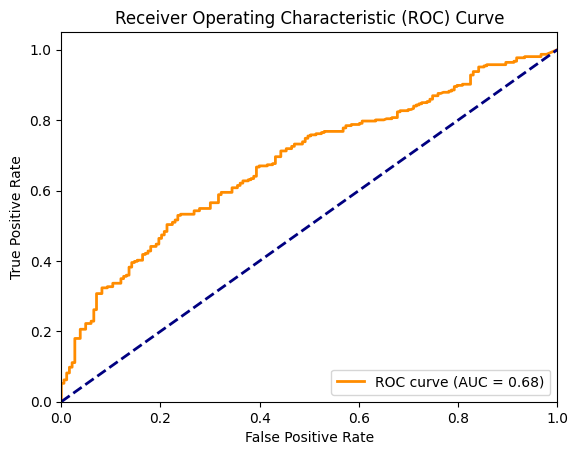
To evaluate fine-grained hallucination detection performance, we compute AUROC of claim-level hallucination detection. Below, we plot the ROC curve and report these results.
[15]:
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, roc_auc_score
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true=all_claim_grades, y_score=all_claim_scores)
roc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_true=all_claim_grades, y_score=all_claim_scores)
[16]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color="darkorange", lw=2, label=f"ROC curve (AUC = {roc_auc:.2f})")
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color="navy", lw=2, linestyle="--")
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel("False Positive Rate")
plt.ylabel("True Positive Rate")
plt.title("Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve")
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
Lastly, we evaluate the gains from uncertainty-aware decoding (UAD) by measuring the factual precision over claims at various filtering thresholds.
[17]:
plot_model_accuracies(scores=all_claim_scores, correct_indicators=all_claim_grades, title="LLM Accuracy by Claim Confidence Threshold", display_percentage=True)
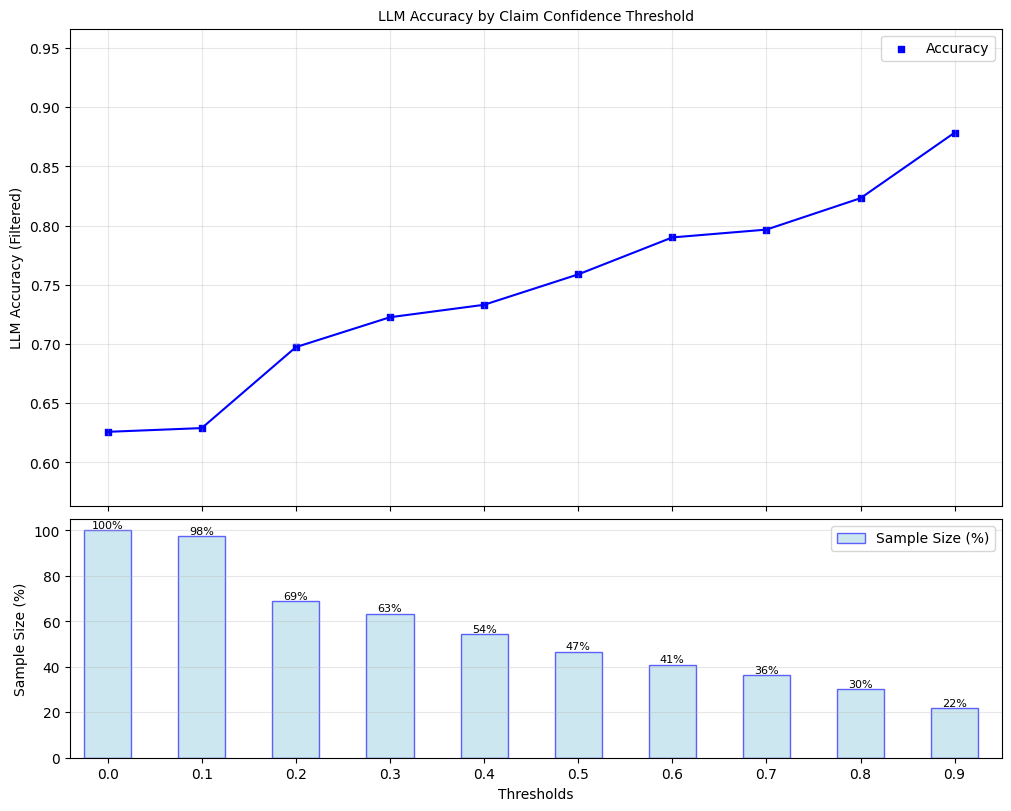
Since, we have selected a threshold of 0.35, we can measure LLM accuracy with and without UAD.
[18]:
thresh = 1 / 3
filtered_grades, filtered_scores = [], []
for grade, score in zip(all_claim_grades, all_claim_scores):
if score > thresh:
filtered_grades.append(grade)
filtered_scores.append(score)
print(f"Baseline LLM factual precision: {np.mean(all_claim_grades)}")
print(f"UAD-Improved LLM factual precision: {np.mean(filtered_grades)}")
Baseline LLM factual precision: 0.6257668711656442
UAD-Improved LLM factual precision: 0.7381818181818182
4. Scorer Definitions#
Long-form uncertainty quantification implements a three-stage pipeline after response generation:
Response Decomposition: The response \(y\) is decomposed into units (claims or sentences), where a unit as denoted as \(s\).
Unit-Level Confidence Scoring: Confidence scores are computed using function \(c_g(s;\cdot) \in [0, 1]\). Higher scores indicate greater likelihood of factual correctness. Units with scores below threshold \(\tau\) are flagged as potential hallucinations.
Response-Level Aggregation: Unit scores are combined to provide an overall response confidence.
Graph-based scorers, proposed by Jiang et al., 2024, decompose original and sampled responses into claims, obtain the union of unique claims across all responses, and compute graph centrality metrics on the bipartite graph of claim-response entailment to measure uncertainty. These scorers operate only at the claim level, as sentences typically contain multiple claims, meaning their union is not well-defined. Formally, we denote a bipartite graph \(G\) with node set \(V = \mathbf{s} \cup \mathbf{y}\), where \(\mathbf{y}\) is a set of \(m\) responses generated from the same prompt and \(\mathbf{s}\) is the union of all unique claims across those decomposed responses. In particular, an edge exists between a claim-response pair \((s, y) \in \mathbf{s} \times \mathbf{y}\) if and only if claim \(s\) is entailed in response \(y\). We define the following graph metrics for claim \(s\):
Degree Centrality - \(\frac{1}{m} \sum_{j=1}^m P(\text{entail}|y_j, s)\) is the average edge weight, measured by entailment probability for claim node \(s\).
Betweenness Centrality - \(\frac{1}{B_{\text{max}}}\sum_{u \neq v \neq s} \frac{\sigma_{uv}(s)}{\sigma_{uv}}\) measures uncertainty by calculating the proportion of shortest paths between node pairs that pass through node \(s\), where \(\sigma_{uv}\) represents all shortest paths between nodes \(u\) and \(v\), and \(B_{\text{max}}\) is the maximum possible value.:nbsphinx-math:footnote{Specifically, $B_{text{max}}=frac{1}{2} [m^2 (p + 1)^2 + m (p + 1)(2t - p - 1) - t (2p - t + 3)]$, $p = frac{(|mathbf{s}| - 1)}{m}$, and $t = (|mathbf{s}| - 1) mod m$.}
Closeness Centrality - \(\frac{m + 2(|\mathbf{s}| - 1) }{\sum_{v \neq s}dist(s, v)}\) measures the inverse sum of distances to all other nodes, normalized by the minimum possible distance.
Harmonic Centrality - \(\frac{1}{H_{\text{max}}}\sum_{v \neq s}\frac{1}{dist(s, v)}\) is the sum of inverse of distances to all other nodes, normalized by the maximum possible value, where \(H_{\text{max}}=m + \frac{ |\mathbf{s}| - 1}{2}\).
Laplacian Centrality - \(\frac{E_L (G)-E_L (G_{\text{-} s})}{E_L (G)}\) is the proportional drop in Laplacian energy \(E_L (G)\) resulting from dropping node \(s\) from the graph, where \(G_{\text{-}s}\) denotes the graph \(G\) with node \(s\) removed, \(E_L (G) = \sum_{i} \lambda_i^2\), and \(\lambda_i\) are the eigenvalues of \(G\)’s Laplacian matrix.
PageRank - $ \frac{1-d}{|V|} + d \sum_{v \in `N(s)} :nbsphinx-math:frac{C_{PR}(v)}{N(v)}`$ is the stationary distribution probability of a random walk with restart probability \((1-d)\), where \(N(s)\) denotes the set of neighboring nodes of \(s\) and \(C_{PR}(v)\) is PageRank of node \(v\).
where \(\mathbf{y}^{(s)}_{\text{cand}} = \{y_1^{(s)}, ..., y_m^{(s)}\}\) are \(m\) candidate responses.
© 2025 CVS Health and/or one of its affiliates. All rights reserved.